给定一个由表示变量之间关系的字符串方程组成的数组,每个字符串方程 equations[i] 的长度为 4,并采用两种不同的形式之一:"a==b" 或 "a!=b"。在这里,a 和 b 是小写字母(不一定不同),表示单字母变量名。
只有当可以将整数分配给变量名,以便满足所有给定的方程时才返回 true,否则返回 false。
示例 1:
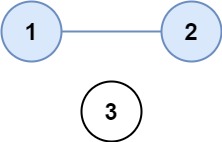
1 2 3 输入:["a==b","b!=a"] 输出:false 解释:如果我们指定,a = 1 且 b = 1,那么可以满足第一个方程,但无法满足第二个方程。没有办法分配变量同时满足这两个方程。
示例 2:
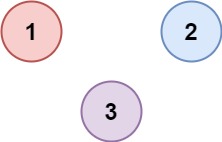
1 2 3 输入:["b==a","a==b"] 输出:true 解释:我们可以指定 a = 1 且 b = 1 以满足满足这两个方程。
示例 3:
1 2 输入:["a==b","b==c","a==c"] 输出:true
示例 4:
1 2 输入:["a==b","b!=c","c==a"] 输出:false
示例 5:
1 2 输入:["c==c","b==d","x!=z"] 输出:true
提示:
1 <= equations.length <= 500equations[i].length == 4equations[i][0] 和 equations[i][3] 是小写字母equations[i][1] 要么是 '=',要么是 '!'equations[i][2] 是 '='
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 public class UF { private int count; private int[] parent; private int[] size; public UF(int n){ this.count = n; parent = new int[n]; size = new int[n]; for (int i =0;i<n;i++){ parent[i] =i; size[i] =1; } } public void union(int p,int q){ int rootP = find(p); int rootQ = find(q); if (rootQ==rootP){ return; } if (size[rootP]>size[rootQ]){ parent[rootQ] = rootP; size[rootP] +=size[rootQ]; }else { parent[rootP] = rootQ; size[rootQ] +=size[rootP]; } count--; } public boolean connected(int p,int q){ int rootQ = find(q); int rootP = find(p); return rootP ==rootQ; } private int find(int x){ while (parent[x]!=x){ parent[x] = parent[parent[x]]; x = parent[x]; } return x; } public int count(){ return count; } } class Solution{ public boolean equationsPossible(String[] equations) { UF uf = new UF(26); for (String eq : equations) { if (eq.charAt(1) == '=') { char x = eq.charAt(0); char y = eq.charAt(3); uf.union(x - 'a', y - 'a'); } } for (String eq : equations) { if (eq.charAt(1) == '!') { char x = eq.charAt(0); char y = eq.charAt(3); if (uf.connected(x - 'a', y - 'a')) { return false; } } } return true; } }
直接使用并查集秒了喵喵喵
2.leetcode 省份数量
有 n 个城市,其中一些彼此相连,另一些没有相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。
省份 是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有相连的城市。
给你一个 n x n 的矩阵 isConnected ,其中 isConnected[i][j] = 1 表示第 i 个城市和第 j 个城市直接相连,而 isConnected[i][j] = 0 表示二者不直接相连。
返回矩阵中 省份 的数量。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]] 输出:2
示例 2:
1 2 输入:isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]] 输出:3
提示:
1 <= n <= 200n == isConnected.lengthn == isConnected[i].lengthisConnected[i][j] 为 1 或 0isConnected[i][i] == 1isConnected[i][j] == isConnected[j][i]
题解:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class DFS { private void dfs(int[] [] isConnected,boolean[] visited,int i){ for (int j=0;j<isConnected.length;j++){ if (isConnected[i][j]==1&&!visited[j]){ visited[j] = true; dfs(isConnected,visited,j); } } } class Solution{ public int findCircleNUm(int[][] isconnected){ int n = isconnected.length; boolean[] visited = new boolean[n]; int provinces = 0; for (int i=0;i<n;i++){ if (!visited[i]){ dfs(isconnected,visited,i); provinces++; } } return provinces; } } }
遍历矩阵 isConnectedis Co nnec te d 。如果 isConnected[i][j] = 1,将 ii 节点和 jj 节点相连。
然后判断每个城市节点的根节点,然后统计不重复的根节点有多少个,也就是集合个数,即为「省份」的数量。
3.leetcode 200. 岛屿数量
给你一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 输入:grid = [ ["1","1","1","1","0"], ["1","1","0","1","0"], ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["0","0","0","0","0"] ] 输出:1
示例 2:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 输入:grid = [ ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["0","0","1","0","0"], ["0","0","0","1","1"] ] 输出:3
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 300grid[i][j] 的值为 '0' 或 '1'
题解:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public class dfs_leetcode { private void dfs(char[][] grid,int i ,int j){ int n = grid.length; int m = grid[0].length; if (i<0||i>=n||j<0||j>=m||grid[i][j]=='0'){ return; } grid[i][j]='0'; dfs(grid, i + 1, j); // 向下 dfs(grid, i - 1, j); // 向上 dfs(grid, i, j + 1); // 向右 dfs(grid, i, j - 1); // 向左 } public int numIslands(char[][] grid){ if (grid==null||grid.length==0){ return 0; } int count = 0; for (int i=0;i<grid.length;i++){ for (int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++){ if (grid[i][j]=='1'){ dfs(grid,i,j); count++; } } } return count; } }
主要就是运用了递归,然后一点一点去找,这个过程就是深度搜索
时间复杂度 :O(m×n)O (m ×n )。其中 mm 和 nn 分别为行数和列数。空间复杂度 :O(m×n)O (m ×n )。
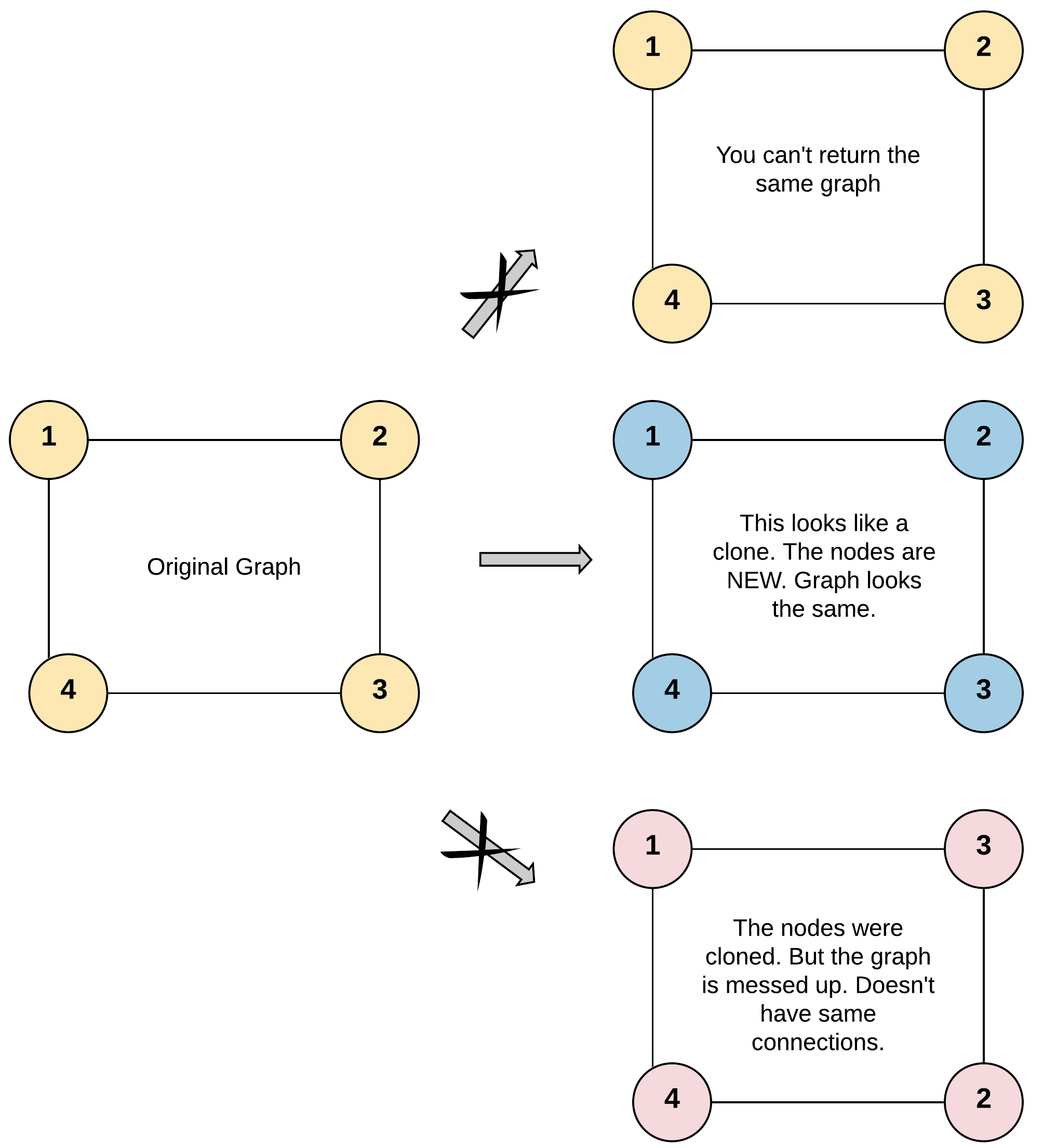
给你无向 连通 深拷贝
图中的每个节点都包含它的值 val(int) 和其邻居的列表(list[Node])。
1 2 3 4 class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; }
测试用例格式:
简单起见,每个节点的值都和它的索引相同。例如,第一个节点值为 1(val = 1),第二个节点值为 2(val = 2),以此类推。该图在测试用例中使用邻接列表表示。
邻接列表 是用于表示有限图的无序列表的集合。每个列表都描述了图中节点的邻居集。
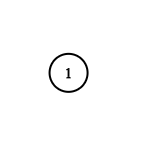
给定节点将始终是图中的第一个节点(值为 1)。你必须将 给定节点的拷贝 作为对克隆图的引用返回。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 输入:adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] 输出:[[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] 解释: 图中有 4 个节点。 节点 1 的值是 1,它有两个邻居:节点 2 和 4 。 节点 2 的值是 2,它有两个邻居:节点 1 和 3 。 节点 3 的值是 3,它有两个邻居:节点 2 和 4 。 节点 4 的值是 4,它有两个邻居:节点 1 和 3 。
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入:adjList = [[]] 输出:[[]] 解释:输入包含一个空列表。该图仅仅只有一个值为 1 的节点,它没有任何邻居。
示例 3:
1 2 3 输入:adjList = [] 输出:[] 解释:这个图是空的,它不含任何节点。
提示:
这张图中的节点数在 [0, 100] 之间。
1 <= Node.val <= 100每个节点值 Node.val 都是唯一的,
图中没有重复的边,也没有自环。
图是连通图,你可以从给定节点访问到所有节点。
题解:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 import java.util.*; class Node{ public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node(){ val = 0; neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } public Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } public Node(int val, List<Node> neighbors) { this.val = val; this.neighbors = neighbors; } } public class cloneGraph { public Node cloneGraph(Node node){ Map<Node,Node> lookup = new HashMap<>(); if (node ==null){ return null; } Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>(); Node clone = new Node(node.val,new ArrayList<>()); lookup.put(node,clone); queue.offer(node); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ Node curr = queue.poll(); for (Node neighbor:curr.neighbors){ if (!lookup.containsKey(neighbor)){ Node neighborClone = new Node(neighbor.val,new ArrayList<>()); lookup.put(neighbor,neighborClone); queue.offer(neighbor); } lookup.get(curr).neighbors.add(lookup.get(neighbor)); } } return clone; } }
时间复杂度 :O(V + E),其中 V 是图中节点的数量,E 是图中边的数量。每个节点和每条边都会被访问一次。
空间复杂度 :O(V),用于存储 lookup 映射表和 BFS 队列。
lookup MapHashMap 用于存储原图中的每个节点及其对应的克隆节点。通过这个映射,我们可以避免多次克隆相同的节点。
空图处理 :如果输入的 node 为 null,则直接返回 null,因为图为空不需要进行克隆。
cloneNode 对象,并将它放入 lookup 映射中,将原节点 node 和它的克隆节点 clone 关联起来。
队列初始化 :创建一个队列 queue,用于广度优先搜索(BFS)。把原图的起始节点 node 加入队列中。
BFS 循环 :当队列非空时,继续从队列中取出节点 curr,并访问它的邻居。
通过这个过程,我们逐渐构建出图的克隆,且保证每个节点和邻居关系都能被正确地克隆出来。