408 数据结构 数据结构 队列字符串篇 mengnankkzhou 2024-09-19 2024-12-16 队列
队列是一种线性数据结构,先进先出 ,队列常用于各种需要顺序处理的场景,如任务调度、资源分配、广度优先搜索等
简单的链式队列实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 public class Linkedqueue { private Node front; private Node rear; private int size; public Linkedqueue(Node front, Node rear, int size) { this.front = front; this.rear = rear; this.size = size; } public boolean isEmpty() { return front == null; } public void enqueue(int date) { Node newNode = new Node(date); if (rear == null) { front = rear = newNode; } else { rear.next = newNode; rear = newNode; } size++; System.out.println("入队元素是" + date); } public int dequeue() { if (isEmpty()) { System.out.println("队列为空"); return -1; } int data = front.data; front = front.next; if (front == null) { rear = null; } size--; System.out.println("出队元素是" + data); return data; } public int peek() { if (isEmpty()) { System.out.println("队列为空"); return -1; } return front.data; } public int getSize() { return size; } }
由于链式队列使用链表存储数据,它没有固定的容量,可以根据需要动态增长。
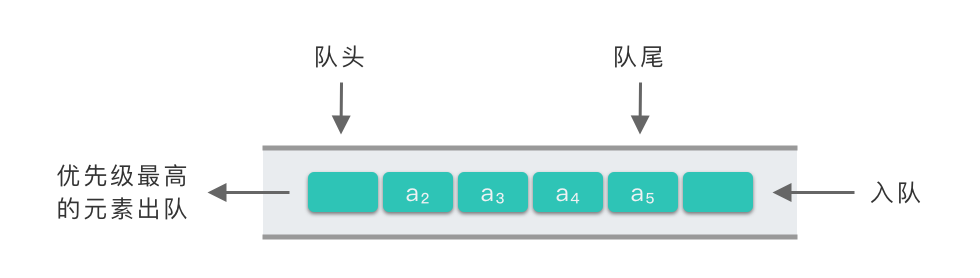
队列还有双端队列和优先队列
优先队列和普通队列的不同点在于出队顺序
优先队列的应用场景非常多,比如:
数据压缩 :赫夫曼编码算法;最短路径算法 :Dijkstra 算法;最小生成树算法 :Prim 算法;任务调度器 :根据优先级执行系统任务;事件驱动仿真 :顾客排队算法;排序问题 :查找第 k 个最小元素。
在java中PriorityQueue类可以用来实现优先队列
默认情况下,它是一个最小堆 ,也就是说,优先级最低的元素会最先出队。我们可以自定义比较器来改变优先级规则,使其成为最大堆。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import java.util.PriorityQueue; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建一个优先队列,默认为最小堆 PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(); // 向队列中插入元素 pq.add(5); pq.add(1); pq.add(3); pq.add(2); pq.add(4); // 打印优先队列中的元素 System.out.println("优先队列中的元素: " + pq); // 获取并移除优先队列中的最小元素 System.out.println("移除的元素: " + pq.poll()); // 查看队头元素(最小元素) System.out.println("队头元素: " + pq.peek()); // 继续移除队列中的元素 while (!pq.isEmpty()) { System.out.println("移除的元素: " + pq.poll()); } } }
简单的队列的使用
那么我们可以自定义一个优先队列
创建一个自定义对象类,包含你要比较的属性。
实现 Comparable 接口或使用 Comparator,定义元素比较的逻辑,以此确定优先级。
使用 PriorityQueue 并传入比较规则。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 import java.util.PriorityQueue; // 任务类,包含任务名、优先级、执行时间 class Task implements Comparable<Task> { private String name; private int priority; // 优先级,值越小优先级越高 private long executionTime; // 执行时间(时间戳) // 构造函数 public Task(String name, int priority, long executionTime) { this.name = name; this.priority = priority; this.executionTime = executionTime; } // 实现 compareTo 方法,首先比较优先级,如果优先级相同,则比较执行时间 @Override public int compareTo(Task other) { if (this.priority != other.priority) { return Integer.compare(this.priority, other.priority); // 优先级小的先处理 } else { return Long.compare(this.executionTime, other.executionTime); // 时间早的先处理 } } @Override public String toString() { return "Task{name='" + name + "', priority=" + priority + ", executionTime=" + executionTime + '}'; } } public class CustomPriorityQueue { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建优先队列,并将 Task 任务对象放入队列 PriorityQueue<Task> taskQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(); // 添加任务,传入任务名称、优先级和执行时间 taskQueue.add(new Task("任务1", 3, System.currentTimeMillis() + 1000)); taskQueue.add(new Task("任务2", 1, System.currentTimeMillis())); taskQueue.add(new Task("任务3", 2, System.currentTimeMillis() + 500)); taskQueue.add(new Task("任务4", 2, System.currentTimeMillis() + 200)); // 依次处理优先队列中的任务 while (!taskQueue.isEmpty()) { System.out.println("处理任务: " + taskQueue.poll()); } } }
先比较优先级,优先级相同再比较时间戳
二叉堆
二叉堆:符合以下两个条件之一的完全二叉树:
大顶堆:根节点值 ≥ 子节点值。
小顶堆:根节点值 ≤ 子节点值。
堆调整方法 heapAdjust :把移走了最大值元素以后的剩余元素组成的序列再构造为一个新的堆积。具体步骤如下:
从根节点开始,自上而下地调整节点的位置,使其成为堆积。即把序号为 ii 的节点与其左子树节点(序号为 2×i2×i )、右子树节点(序号为 2×i+12×i +1)中值最大的节点交换位置。
因为交换了位置,使得当前节点的左右子树原有的堆积特性被破坏。于是,从当前节点的左右子树节点开始,自上而下继续进行类似的调整。
如此下去直到整棵完全二叉树成为一个大顶堆。
将数组构建为二叉堆方法(初始堆建立方法) heapify :
如果原始序列对应的完全二叉树(不一定是堆)的深度为 dd ,则从 d−1d −1 层最右侧分支节点(序号为 ⌊n2⌋⌊2n ⌋)开始,初始时令 i=⌊n2⌋i =⌊2n ⌋,调用堆调整算法。
每调用一次堆调整算法,执行一次 i=i−1i =i −1,直到 i==1i ==1 时,再调用一次,就把原始数组构建为了一个二叉堆。
字符串
简称为串,是由零个或多个字符组成的有限序列。一般记为 s=a1a2…an(0≤n⪇∞)s =a 1a 2…a**n (0≤n ⪇∞)。
字符串名称 :字符串定义中的 ss 就是字符串的名称。字符串的值 :a1a2…ana 1a 2…a**n 组成的字符序列就是字符串的值,一般用双引号括起来。字符变量 :字符串每一个位置上的元素都是一个字符变量。字符 aia**i 可以是字母、数字或者其他字符。ii 是该字符在字符串中的位置。字符串的长度 :字符串中字符的数目 nn 称为字符串的长度。空串 :零个字符构成的串也成为 「空字符串(Null String)」 ,它的长度为 00,可以表示为 ""。子串 :字符串中任意个连续的字符组成的子序列称为该字符串的 「子串(Substring)」 。并且有两种特殊子串,起始于位置为 00、长度为 kk 的子串称为 「前缀(Prefix)」 。而终止于位置 n−1n −1、长度为 kk 的子串称为 「后缀(Suffix)」 。主串 :包含子串的字符串相应的称为 「主串」 。
举例
str 是字符串的变量名称,Hello World是该字符串的值,其字符串的长度为11。
从前面开始是0-n-1,然后从后面开始是-1-以此类推
字符串一般作为一个整体来使用
关于字符串的问题一般有这几种
根据字符串的特点,我们可以将字符串问题分为以下几种:
字符串匹配问题。
子串相关问题。
前缀 / 后缀相关问题;
回文串相关问题。
子序列相关问题。
字符串 str1 = "abc" 和 str2 = "acc",它们的第一个字母都是 aa ,而第二个字母,由于字母 bb 比字母 cc 要靠前,所以 b<cb <c ,于是我们可以说 "abc" < "acd" ,也可以说 str1<str2。
字符串相等的情况:
str1和str2的长度相等
str1和str2对应位置上的各个字符都相等
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class stcmp { public static int strcmp(String str1,String str2){ int index1 = 0,index2 = 0; while (index1<str1.length()&&index2<str2.length()) if (str1.charAt(index1)==str2.charAt(index2)){ index1++; index2++; }else if (str1.charAt(index1)<str2.charAt(index2)){ return -1; }else { return 1; } if (str1.length()<str2.length()){ return -1; }else if (str1.length()>str2.length()){ return 1; } else { return 0; } } }
自定义字符串的比较
字符串的字符编码
计算机中常用字符使用的 ASCII 编码为例。最早的时候,人们制定了一个包含 127127 个字符的编码表 ASCII 到计算机系统中。ASCII 编码表中的字符包含了大小写的英文字母、数字和一些符号。每个字符对应一个编码,比如大写字母 A 的编码是 65,小写字母 a 的编码是 97。
GB2312、GBK、GB18030这几个是我国定制的中文编码
Unicode 编码是现在国际上最常用的
Unicode 编码最常用的就是 UTF-8 编码,UTF-8 编码把一个 Unicode 字符根据不同的数字大小编码成 1∼61∼6 个字节,常用的英文字母被编码成 11 个字节,汉字通常是 33 个字节。
存储结构
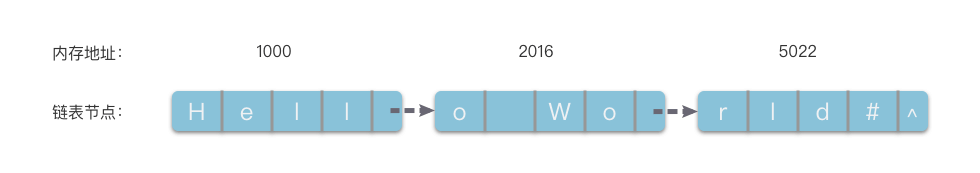
符串的链式存储将一组任意的存储单元串联在一起。链节点之间的逻辑关系是通过指针来间接反映的。
还有顺序存储结构,物理地址上是相连的
字符串的匹配问题