javase java Javase学习基础(1) mengnankkzhou 2024-04-23 2024-08-20 java basic
1.面对对象
1.类和对象
属性,即可以设置的一些属性
方法即可以进行的一些行为
2.变量
java中有八种基本类型,这八种都是关键字,在设置变量时不能够用这些关键字。
这八种分别是:
整型 (4种)
1.整型
类型
缺省值
长度
范围
byte
0
8
-128~127
short
0
16
-32768~32767
int
0
32
-2147483648~2147483647
long
0
64
-9223372036854~9223372036854
2.字符型
char 类型用于存放一个字符,值用单引号表示(双引号表示字符串)
3.浮点型
注意: 默认的小数值是double类型的 加一个字母f ,直接把该数字声明成float类型f ,
4.布尔型
布尔型表示真假,其长度为1
true false
5.Sting
字面型:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { String name = "盖伦" ; char a= 'c' ; char tab = '\t' ; char carriageReturn = '\r' ; char newLine = '\n' ; char doubleQuote = '\"' ; char singleQuote = '\'' ; char backslash = '\\' ;
类型转换
规则:从小到大自动转,从大到小强制转
作用域
如果一个变量,是声明在一个方法上的,就叫做参数
声明在方法内的变量,叫做局部变量
final
准确的描述是 当一个变量被final修饰的时候,该变量只有一次赋值的机会
3.操作符
scanner操作符(向控制台输入数据)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import java.util.Scanner; public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner (System.in); float a = s.nextFloat(); System.out.println("读取的浮点数的值是:" +a); } } import java.util.Scanner;Scanner s = new Scanner (System.in);
要先引用。
字符串时LIne
注意:需要注意的是,如果在通过nextInt()读取了整数后,再接着读取字符串,读出来的是回车换行:“\r\n”,因为nextInt仅仅读取数字信息,而不会读取 回车换行"\r\n".
所以,如果在业务上需要读取了整数后,接着读取字符串,那么就应该连续执行两次nextLine(),第一次是取走回车换行,第二次才是读取真正的字符串import java.util.Scanner;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 import java.util.Scanner; public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner (System.in); int i = s.nextInt(); System.out.println("读取的整数是" + i); String rn = s.nextLine(); String a = s.nextLine(); System.out.println("读取的字符串是:" +a); } }
算数
如果任何运算单元的长度都不超过int,那么运算结果就按照int来计算
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { byte a = 1 ; byte b= 2 ; byte c = (byte ) (a+b); int d = a+b; } }
逻辑运算符
&&与&
无论长路与还是短路与
||与|
无论长路或还是短路或
!
取反!
^
异或^
位操作符
位或
5的二进制是101
位与
5的二进制是101
异或
5的二进制是101
一些特别情况:
取非
5 的二进制是 00000101
左移右移
左移:根据一个整数的二进制表达,将其每一位都向左移动,最右边一位补0
java三元操作符
表达式?值1:值2
4.java控制流程
if语句
if else语句
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { boolean b = false ; if (b) System.out.println("yes" ); else System.out.println("no" ); } }
else if 是多条件判断
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int i = 2 ; if (i==1 ) System.out.println(1 ); if (i==2 ) System.out.println(2 ); if (i==3 ) System.out.println(3 ); if (i==4 ) System.out.println(4 ); if (i==1 ) System.out.println(1 ); else if (i==2 ) System.out.println(2 ); else if (i==3 ) System.out.println(3 ); else if (i==4 ) System.out.println(4 ); } }
swich语句
switch可以使用byte,short,int,char,String,enum
注: 每个表达式结束,都应该有一个break;注: String在Java1.7之前是不支持的, Java从1.7开始支持switch用String的,编译后是把String转化为hash值,其实还是整数
while和do while循环
while
条件为true时 重复执行
示例代码
do while
条件为true时 重复执行,至少会执行一次
for循环
和c语言一样 for
1 for (int j = 0 ; j < 10 ; j++)
continue
继续进行下一次循环
结束循环
结束当前循环:break
使用boolean变量结束外部循环
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { boolean breakout = false ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 10 ; j++) { System.out.println(i + ":" + j); if (0 == j % 2 ) { breakout = true ; break ; } } if (breakout) break ; } } }
使用标签结束外部循环
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { outloop: for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 10 ; j++) { System.out.println(i+":" +j); if (0 ==j%2 ) break outloop; } } } }
5.数组
声明数组-创建数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] a; a = new int [5 ]; int [] b = new int [5 ]; } }
数组的第一个数是从0开始的,.length属性 用于访问一个数组的长度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] a; a = new int [5 ]; System.out.println(a.length); a[4 ]=100 ; a[5 ]=101 ; } }
随机获得整数
1 (int) (Math.random() * 100)
初始化数组
作为int类型的数组,默认值是0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] a = new int []{100 ,102 ,444 ,836 ,3236 }; int [] b = {100 ,102 ,444 ,836 ,3236 }; int [] c = new int [3 ]{100 ,102 ,444 ,836 ,3236 }; } }
排序
选择排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int a [] = new int []{18 ,62 ,68 ,82 ,65 ,9 }; for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " " ); } System.out.println(" " ); for (int i = 1 ; i < a.length; i++) { if (a[i]<a[0 ]){ int temp = a[0 ]; a[0 ] = a[i]; a[i] = temp; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " " ); } System.out.println(" " ); for (int i = 2 ; i < a.length; i++) { if (a[i]<a[1 ]){ int temp = a[1 ]; a[1 ] = a[i]; a[i] = temp; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " " ); } System.out.println(" " ); for (int j = 0 ; j < a.length-1 ; j++) { for (int i = j+1 ; i < a.length; i++) { if (a[i]<a[j]){ int temp = a[j]; a[j] = a[i]; a[i] = temp; } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " " ); } System.out.println(" " ); } }
冒泡排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int a [] = new int []{18 ,62 ,68 ,82 ,65 ,9 }; for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " " ); } System.out.println(" " ); for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length-1 ; i++) { if (a[i]>a[i+1 ]){ int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[i+1 ]; a[i+1 ] = temp; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " " ); } System.out.println(" " ); for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length-2 ; i++) { if (a[i]>a[i+1 ]){ int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[i+1 ]; a[i+1 ] = temp; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " " ); } System.out.println(" " ); for (int j = 0 ; j < a.length; j++) { for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length-j-1 ; i++) { if (a[i]>a[i+1 ]){ int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[i+1 ]; a[i+1 ] = temp; } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " " ); } System.out.println(" " ); } }
增强型for循环
注:增强型for循环只能用来取值,却不能用来修改数组里的值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int values [] = new int []{18 ,62 ,68 ,82 ,65 ,9 }; for (int i = 0 ; i < values.length; i++) { int each = values[i]; System.out.println(each); } for (int each : values) { System.out.println(each); } } }
复制数组
把一个数组的值,复制到另一个数组中
System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int a [] = new int []{18 ,62 ,68 ,82 ,65 ,9 }; int b[] = new int [3 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < b.length; i++) { b[i] = a[i]; } System.arraycopy(a, 0 , b, 0 , 3 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < b.length; i++) { System.out.print(b[i] + " " ); } } }
练习复制数组:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 import javax.management.MXBean;import java.util.Arrays;public class Arrs { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] arr_0; int [] arr_1; while (true ) { int temp = (int ) (Math.random() * 10 ) + 1 ; if (temp >5 && temp < 10 ) { arr_0 = new int [temp]; break ; } } while (true ) { int temp = (int ) (Math.random() * 10 ) + 1 ; if (temp >5 && temp < 10 ) { arr_1 = new int [temp]; break ; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < arr_0.length; i++) arr_0[i] = (int ) (Math.random() * 100 ) + 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr_0.length; i++) arr_1[i] = (int ) (Math.random() * 100 ) + 1 ; int [] new_arr = new int [arr_0.length + arr_1.length]; System.arraycopy(arr_0,0 ,new_arr,0 ,arr_0.length); System.arraycopy(arr_1,0 ,new_arr,arr_0.length,arr_1.length); System.out.println(arr_0.length); System.out.println(arr_1.length); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr_0)); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr_1)); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(new_arr)); System.out.println("Done" ); } }
二维数组
这是一个二维数组 ,里面的每一个元素,都是一个一维数组
1 2 3 4 5 int b[][] = new int [][]{ {1 ,2 ,3 }, {4 ,5 ,6 }, {7 ,8 ,9 } };
初始化二维数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int [][] a = new int [2 ][3 ]; a[1 ][2 ] = 5 ; int [][] b = new int [2 ][]; b[0 ] =new int [3 ]; b[0 ][2 ] = 5 ; int [][] c = new int [][]{ {1 ,2 ,4 }, {4 ,5 }, {6 ,7 ,8 ,9 } }; } }
Arrays
关键字
简介
示例代码
copyOfRange
数组复制
示例代码
toString()
转换为字符串
示例代码
sort
排序
示例代码
binarySearch
搜索
示例代码
equals
判断是否相同
示例代码
fill
填充
数组复制
System.arraycopy,需要事先准备好目标数组,并分配长度。 copyOfRange 只需要源数组就就可以了,通过返回值,就能够得到目标数组了。第3个参数 ,表示源数组的结束位置,是取不到的 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import java.util.Arrays; public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int a[] = new int [] { 18 , 62 , 68 , 82 , 65 , 9 }; int [] b = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, 0 , 3 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < b.length; i++) { System.out.print(b[i] + " " ); } } }
转换为字符串
Arrays提供了一个toString()方法,直接把一个数组,转换为字符串,这样方便观察数组的内容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import java.util.Arrays; public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int a[] = new int [] { 18 , 62 , 68 , 82 , 65 , 9 }; String content = Arrays.toString(a); System.out.println(content); } }
排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 import java.util.Arrays; public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int a[] = new int [] { 18 , 62 , 68 , 82 , 65 , 9 }; System.out.println("排序之前 :" ); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); Arrays.sort(a); System.out.println("排序之后:" ); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } }
搜索
需要注意的是,使用binarySearch进行查找之前,必须使用sort进行排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 import java.util.Arrays; public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int a[] = new int [] { 18 , 62 , 68 , 82 , 65 , 9 }; Arrays.sort(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); System.out.println("数字 62出现的位置:" +Arrays.binarySearch(a, 62 )); } }
判断是否相同
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import java.util.Arrays; public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int a[] = new int [] { 18 , 62 , 68 , 82 , 65 , 9 }; int b[] = new int [] { 18 , 62 , 68 , 82 , 65 , 8 }; System.out.println(Arrays.equals(a, b)); } }
填充
使用同一个值,填充整个数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import java.util.Arrays; public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { int a[] = new int [10 ]; Arrays.fill(a, 5 ); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } }
6.类和对象
引用
引用的概念,如果一个变量的类型是 类类型,而非基本类型,那么该变量又叫做引用。
h这个变量是Hero类型,又叫做引用代表 右侧创建的对象代表 ” 在面向对象里,又叫做“指向 ”
引用有多个,但是对象只有一个。
一个引用,多个对象时,只有最后一个能成功指向
继承
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class Weapon extends Item { int damage; public static void main (String[] args) { Weapon infinityEdge = new Weapon (); infinityEdge.damage = 65 ; infinityEdge.name = "无尽之刃" ; infinityEdge.price = 3600 ; } }
通过继承别的类的属性,不需要重复设计。
方法重载
方法名是一样的,但是参数类型不一样
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public class ADHero extends Hero { public void attack () { System.out.println(name + " 进行了一次攻击 ,但是不确定打中谁了" ); } public void attack (Hero h1) { System.out.println(name + "对" + h1.name + "进行了一次攻击 " ); } public void attack (Hero h1, Hero h2) { System.out.println(name + "同时对" + h1.name + "和" + h2.name + "进行了攻击 " ); } public static void main (String[] args) { ADHero bh = new ADHero (); bh.name = "赏金猎人" ; Hero h1 = new Hero (); h1.name = "盖伦" ; Hero h2 = new Hero (); h2.name = "提莫" ; bh.attack(h1); bh.attack(h1, h2); } }
构造方法
方法名和类名一样(包括大小写)没有返回类型
一旦提供了一个有参的构造方法没有显式 的提供一个无参的构造方法
this
this即代表当前对象
1 2 3 //直接打印对象,会显示该对象在内存中的虚拟地址 ``//格式:Hero@c17164 c17164即虚拟地址,每次执行,得到的地址不一定一样 而调用行为则出现相同的地址
属性名和变量名不能一样
参数名不得不使用其他变量名
用this即可解决问题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public class Hero { String name; float hp; float armor; int moveSpeed; public void setName1 (String name) { name = name; } public void setName2 (String heroName) { name = heroName; } public void setName3 (String name) { this .name = name; } public static void main (String[] args) { Hero h = new Hero (); h.setName1("teemo" ); System.out.println(h.name); h.setName2("garen" ); System.out.println(h.name); h.setName3("死歌" ); System.out.println(h.name); } }
传参
传参分为基本类型传参 和类类型传参
基本:
基本类型传参
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public class Hero { String name; float hp; float armor; int moveSpeed; public Hero () { } public void huixue (int xp) { hp = hp + xp; xp=0 ; } public Hero (String name,float hp) { this .name = name; this .hp = hp; } public static void main (String[] args) { Hero teemo = new Hero ("提莫" ,383 ); int xueping = 100 ; teemo.huixue(xueping); System.out.println(xueping); } }
引用和=
果一个变量是基本类型=表示赋值的意思 。引用 。=不再是赋值的意思 =表示指向的意思
类类型传参:
类类型又叫引用 teemo 与 第17行的引用hero ,是不同的引用 两个引用都指向了同一个对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class Hero { String name; float hp; float armor; int moveSpeed; public Hero (String name, float hp) { this .name = name; this .hp = hp; } public void attack (Hero hero, int damage) { hero.hp = hero.hp - damage; } public static void main (String[] args) { Hero teemo = new Hero ("提莫" , 383 ); Hero garen = new Hero ("盖伦" , 616 ); garen.attack(teemo, 100 ); System.out.println(teemo.hp); } }
包
package
把比较接近的类,规划在同一个包下
在最开始的地方声明该类所处于的包名
使用同一个包下的其他类,直接使用即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package charactor; import property.Weapon; public class Hero { String name; float hp; float armor; int moveSpeed; public void equip (Weapon w) { } }
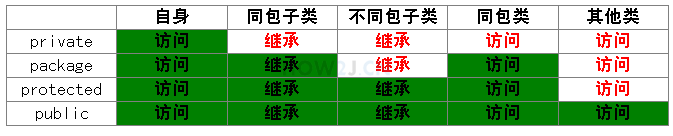
访问修饰符
成员变量有四种修饰符
private 私有的package /friendly/default 不写protected 受保护的public 公共的
类之间的关系
自身:指的是Hero自己同包子类:ADHero这个类是Hero的子类,并且和Hero处于 同一个包下 不同包子类:Support这个类是Hero的子类,但是在 另一个包下 同包类: GiantDragon 这个类和Hero是 同一个包 ,但是彼此没有继承关系 在不同包 ,也没有继承关系的类
类属性
当一个属性被static 修饰的时候,就叫做类属性 ,又叫做静态属性 所有的对象,都共享一个值
如果一个属性声明成类属性,那么所有的对象,都共享这么一个值
所以类属性是可以被用作所有对象都一致的
类方法
类方法: 又叫做静态方法
对象方法: 又叫实例方法,非静态方法
访问一个对象方法,必须建立在有一个对象 的前提的基础上不需要对象 的存在,直接就访问
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 package charactor; public class Hero { public String name; protected float hp; public void die () { hp = 0 ; } public static void battleWin () { System.out.println("battle win" ); } public static void main (String[] args) { Hero garen = new Hero (); garen.name = "盖伦" ; garen.die(); Hero teemo = new Hero (); teemo.name = "提莫" ; Hero.battleWin(); } }
单例模式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 package charactor; public class GiantDragon { private GiantDragon () { } private static GiantDragon instance = new GiantDragon (); public static GiantDragon getInstance () { return instance; } }
枚举
枚举enum是一种特殊的类(还是类),使用枚举可以很方便的定义常
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { Season season = Season.SPRING; switch (season) { case SPRING: System.out.println("春天" ); break ; case SUMMER: System.out.println("夏天" ); break ; case AUTUMN: System.out.println("秋天" ); break ; case WINTER: System.out.println("冬天" ); break ; } } }枚举enum 是一种特殊的类(还是类),使用枚举可以很方便的定义常
1 2 3 public enum Season { SPRING,SUMMER,AUTUMN,WINTER }
7.接口和继承
super
实例化子类,父类的构造方法一定会被调用
其父类的构造方法也会被调用 并且是父类构造方法先调用 子类构造方法会默认调用父类的 无参的构造方法
父类显式提供两个构造方法
分别是无参的构造方法和带一个参数的构造方法
使用关键字super 显式调用父类带参的构造方法
object
声明一个类的时候,默认是继承了Objectextends Object ,object是所有类的父类
Object类提供一个toString方法,所以所有的类都有toString方法字符串表达
通过 System.out.println 打印对象就是打印该对象的toString()返回值
当一个对象没有任何引用指向的时候,它就满足垃圾回收的条件
当它被垃圾回收的时候,它的finalize() 方法就会被调用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 package charactor; public class Hero { public String name; protected float hp; public String toString () { return name; } public void finalize () { System.out.println("这个英雄正在被回收" ); } public static void main (String[] args) { Hero h; for (int i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) { h = new Hero (); } } }
equals() 用于判断两个对象的内容是否相同
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package charactor; public class Hero { public String name; protected float hp; public boolean equals (Object o) { if (o instanceof Hero){ Hero h = (Hero) o; return this .hp == h.hp; } return false ; } public static void main (String[] args) { Hero h1= new Hero (); h1.hp = 300 ; Hero h2= new Hero (); h2.hp = 400 ; Hero h3= new Hero (); h3.hp = 300 ; System.out.println(h1.equals(h2)); System.out.println(h1.equals(h3)); } }
==
用于判断两个引用,是否指向了同一个对象
hashcode
hashCode方法返回一个对象的哈希值
final
当Hero被修饰成final的时候,表示Hero不能够被继承
Hero的useItem方法被修饰成final,那么该方法在ADHero中,不能够被重写
final修饰基本类型变量,表示该变量只有一次赋值机会
inal修饰引用1 次指向对象的机会
抽象类
在类中声明一个方法,这个方法没有实现体,是一个“空”方法
这样的方法就叫抽象方法,使用修饰符“abstract"
当一个类有抽象方法的时候,该类必须被声明为抽象类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 package charactor; public abstract class Hero { String name; float hp; float armor; int moveSpeed; public static void main (String[] args) { } public abstract void attack () ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 package charactor; public class ADHero extends Hero implements AD { public void physicAttack () { System.out.println("进行物理攻击" ); } @Override public void attack () { physicAttack(); } }
Hero类可以在不提供抽象方法的前提下,声明为抽象类
区别1:多个 接口
内部类
内部类分为四种:
非静态内部类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 package charactor; public class Hero { private String name; float hp; float armor; int moveSpeed; class BattleScore { int kill; int die; int assit; public void legendary () { if (kill >= 8 ) System.out.println(name + "超神!" ); else System.out.println(name + "尚未超神!" ); } } public static void main (String[] args) { Hero garen = new Hero (); garen.name = "盖伦" ; BattleScore score = garen.new BattleScore (); score.kill = 9 ; score.legendary(); } }
静态内部类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 package charactor; public class Hero { public String name; protected float hp; private static void battleWin () { System.out.println("battle win" ); } static class EnemyCrystal { int hp=5000 ; public void checkIfVictory () { if (hp==0 ){ Hero.battleWin(); System.out.println(name + " win this game" ); } } } public static void main (String[] args) { Hero.EnemyCrystal crystal = new Hero .EnemyCrystal(); crystal.checkIfVictory(); } }
在一个类里面声明一个静态内部类静态内部类 水晶类的实例化 不需要一个外部类的实例为基础 ,可以直接实例化new 外部类.静态内部类(); 不可以访问外部类的实例属性和方法 私有静态成员外 ,静态内部类和普通类没什么大的区别
匿名类
匿名类指的是在声明一个类的同时实例化它 ,使代码更加简洁精练
有的时候,为了快速使用,直接实例化一个抽象类,并“当场 ”实现其抽象方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package charactor; public abstract class Hero { String name; float hp; float armor; int moveSpeed; public abstract void attack () ; public static void main (String[] args) { ADHero adh=new ADHero (); adh.attack(); System.out.println(adh); Hero h = new Hero (){ public void attack () { System.out.println("新的进攻手段" ); } }; h.attack(); System.out.println(h); } }
本地类
本地类可以理解为有名字的匿名类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 package charactor; public abstract class Hero { String name; float hp; float armor; int moveSpeed; public abstract void attack () ; public static void main (String[] args) { class SomeHero extends Hero { public void attack () { System.out.println( name+ " 新的进攻手段" ); } } SomeHero h = new SomeHero (); h.name ="地卜师" ; h.attack(); } }
默认方法
默认方法是JDK8新特性,指的是接口也可以提供具体方法了,而不像以前,只能提供抽象方法.
8.数字和字符串
数字封装类
数字封装类有
不需要调用构造方法,通过=符号****自动 把 基本类型 转换为 类类型 就叫装箱
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 package digit; public class TestNumber { public static void main (String[] args) { int i = 5 ; Integer it = new Integer (i); Integer it2 = i; } }
不需要调用Integer的intValue方法,通过=就自动转换成int类型,就叫拆箱
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 package digit; public class TestNumber { public static void main (String[] args) { int i = 5 ; Integer it = new Integer (i); int i2 = it.intValue(); int i3 = it; } }
nt的最大值可以通过其对应的封装类Integer.MAX_VALUE获取
字符串
数字转字符串:
方法1: 使用String类的静态方法valueOf
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 package digit; public class TestNumber { public static void main (String[] args) { int i = 5 ; String str = String.valueOf(i); Integer it = i; String str2 = it.toString(); } }
调用Integer的静态方法parseInt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 package digit; public class TestNumber { public static void main (String[] args) { String str = "999" ; int i= Integer.parseInt(str); System.out.println(i); } }
java.lang.Math
数学方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 package digit; public class TestNumber { public static void main (String[] args) { float f1 = 5.4f ; float f2 = 5.5f ; System.out.println(Math.round(f1)); System.out.println(Math.round(f2)); System.out.println(Math.random()); System.out.println((int )( Math.random()*10 )); System.out.println(Math.sqrt(9 )); System.out.println(Math.pow(2 ,4 )); System.out.println(Math.PI); System.out.println(Math.E); } }
格式化
%s 表示字符串
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package digit; public class TestNumber { public static void main (String[] args) { String name = "盖伦" ; int kill = 8 ; String title="超神" ; String sentence = name+ " 在进行了连续 " + kill + " 次击杀后,获得了 " + title +" 的称号" ; System.out.println(sentence); String sentenceFormat = "%s 在进行了连续 %d 次击杀后,获得了 %s 的称号%n" ; System.out.printf(sentenceFormat,name,kill,title);
printf
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 package digit; public class TestNumber { public static void main (String[] args) { String name = "盖伦" ; int kill = 8 ; String title="超神" ; String sentenceFormat = "%s 在进行了连续 %d 次击杀后,获得了 %s 的称号%n" ; System.out.printf(sentenceFormat,name,kill,title); System.out.format(sentenceFormat,name,kill,title); } }
换行符 就是另起一行 — ‘\n’ 换行(newline)回车符 就是回到一行的开头 — ‘\r’ 回车(return)回车换行符
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 package digit; import java.util.Locale; public class TestNumber { public static void main (String[] args) { int year = 2020 ; System.out.format("%d%n" ,year); System.out.format("%8d%n" ,year); System.out.format("%-8d%n" ,year); System.out.format("%08d%n" ,year); System.out.format("%,8d%n" ,year*10000 ); System.out.format("%.2f%n" ,Math.PI); System.out.format(Locale.FRANCE,"%,.2f%n" ,Math.PI*10000 ); System.out.format(Locale.US,"%,.2f%n" ,Math.PI*10000 ); System.out.format(Locale.UK,"%,.2f%n" ,Math.PI*10000 ); } }
字符:
保存一个字符的时候使用char
char对应的封装类是Character
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 package character; public class TestChar { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println(Character.isLetter('a' )); System.out.println(Character.isDigit('a' )); System.out.println(Character.isWhitespace(' ' )); System.out.println(Character.isUpperCase('a' )); System.out.println(Character.isLowerCase('a' )); System.out.println(Character.toUpperCase('a' )); System.out.println(Character.toLowerCase('A' )); String a = 'a' ; String a2 = Character.toString('a' ); } }
length方法返回当前字符串的长度
charAt
获取字符
示例代码
toCharArray
获取对应的字符数组
示例代码
subString
截取子字符串
示例代码
split
分隔
示例代码
trim
去掉首尾空格
示例代码
toLowerCase toUpperCase
大小写
示例代码
indexOf lastIndexOf contains
定位
示例代码
replaceAll replaceFirst
使用equals进行字符串内容的比较,必须大小写一致
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 package character; public class TestString { public static void main (String[] args) { String str1 = "the light" ; String start = "the" ; String end = "Ight" ; System.out.println(str1.startsWith(start)); System.out.println(str1.endsWith(end)); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 package character; public class TestString { public static void main (String[] args) { String str1 = "let there " ; StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer (str1); sb.append("be light" ); System.out.println(sb); sb.delete(4 , 10 ); System.out.println(sb); sb.insert(4 , "there " ); System.out.println(sb); sb.reverse(); System.out.println(sb); } }
时间日历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package date; import java.util.Date; public class TestDate { public static void main (String[] args) { Date d1 = new Date (); System.out.println("当前时间:" ); System.out.println(d1); System.out.println(); Date d2 = new Date (5000 ); System.out.println("从1970年1月1日 早上8点0分0秒 开始经历了5秒的时间" ); System.out.println(d2); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 package date; import java.util.Date; public class TestDate { public static void main (String[] args) { Date now= new Date (); System.out.println("当前时间:" +now.toString()); System.out.println("当前时间getTime()返回的值是:" +now.getTime()); Date zero = new Date (0 ); System.out.println("用0作为构造方法,得到的日期是:" +zero); } }
1 System.out.println("System.currentTimeMillis() \t返回值: "+System.currentTimeMillis());
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package ` `date; import ` `java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import ` `java.util.Date; public ` `class` `TestDate { ``public ` `static ` `void ` `main(String[] args) { `` `` `` `` `` `` `` `` ``SimpleDateFormat sdf = ``new ` `SimpleDateFormat(``"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS" ` `); ``Date d= ``new ` `Date(); ``String str = sdf.format(d); ``System.out.println(``"当前时间通过 yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS 格式化后的输出: " ``+str); ``SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = ``new ` `SimpleDateFormat(``"yyyy-MM-dd" ` `); ``Date d1= ``new ` `Date(); ``String str1 = sdf1.format(d1); ``System.out.println(``"当前时间通过 yyyy-MM-dd 格式化后的输出: " ``+str1); ``} }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 package date; import java.util.Calendar;import java.util.Date; public class TestDate { public static void main (String[] args) { Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance(); Date d = c.getTime(); Date d2 = new Date (0 ); c.setTime(d2); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 package date; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import java.util.Calendar;import java.util.Date; public class TestDate { private static SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat ("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" ); public static void main (String[] args) { Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance(); Date now = c.getTime(); System.out.println("当前日期:\t" + format(c.getTime())); c.setTime(now); c.add(Calendar.MONTH, 1 ); System.out.println("下个月的今天:\t" +format(c.getTime())); c.setTime(now); c.add(Calendar.YEAR, -1 ); System.out.println("去年的今天:\t" +format(c.getTime())); c.setTime(now); c.add(Calendar.MONTH, -1 ); c.set(Calendar.DATE, 3 ); System.out.println("上个月的第三天:\t" +format(c.getTime())); } private static String format (Date time) { return sdf.format(time); } }